Are you looking to make a positive impact on the planet while transforming your space into a lush, thriving oasis? Shades of Green Permaculture might just be the solution you’ve been searching for.
Imagine stepping into your backyard and being greeted by the soothing rustle of leaves, the gentle buzz of pollinators, and the fresh scent of earth. This isn't just a dream; it's a reality you can create. By exploring the world of permaculture, you'll discover how to design a sustainable environment that not only benefits you but also supports the ecosystem around you.
With simple, actionable steps, you can turn any patch of land into a self-sustaining paradise. Ready to dive into the vibrant world of Shades of Green Permaculture and unlock the secrets to a more sustainable lifestyle? Let's get started!
What Is Green Permaculture?
Green permaculture is a thoughtful design system. It focuses on sustainable living. This method uses nature's patterns and strategies. It integrates them into human activities. Green permaculture aims to create self-sufficient ecosystems. These systems nurture the environment and people. It brings harmony between human life and nature.
Understanding The Basics Of Green Permaculture
Green permaculture involves practical techniques. These techniques reduce waste and energy use. It promotes biodiversity and soil health. The system values resources and their efficient use. It aims to minimize human impact on nature.
Core Principles Of Green Permaculture
Green permaculture follows several key principles. These include care for the earth. Care for people is another core principle. It also encourages fair sharing of resources. These principles guide the design of sustainable systems.
The Role Of Nature In Green Permaculture
Nature plays a vital role in green permaculture. It serves as a model for sustainable practices. The system uses natural cycles to build healthy ecosystems. Natural processes inspire solutions for human challenges.
Green permaculture offers many benefits. It promotes healthy food production. It reduces environmental degradation. The system supports community resilience. It fosters a connection between people and nature.

Credit: shadesofgreenpermaculture.com
Principles Of Permaculture
Permaculture is a design system for sustainable living. It mimics natural ecosystems. The principles guide the creation of resilient systems. These systems can sustain human needs. They respect the environment, too. Let’s explore some key principles.
Observe And Interact
Observation is the first step. Understand the environment before acting. Interacting with nature helps find solutions. Nature offers lessons. We just need to notice them.
Catch And Store Energy
Energy is everywhere. Sunlight, water, and wind are energy sources. Storing energy helps during scarce times. Think rain barrels for water. Or solar panels for electricity.
Obtain A Yield
Every system should produce a benefit. This could be food, fuel, or fiber. The aim is to meet human needs. Without harming the planet.
Apply Self-regulation And Accept Feedback
Systems need checks and balances. Self-regulation ensures sustainability. Feedback highlights what works. And what needs change. Listening leads to improvement.
Use And Value Renewable Resources
Nature provides endless resources. Wind, sun, and rain are examples. Using renewables reduces waste. Protects the planet’s health. Always choose sustainable options.
Produce No Waste
Waste is a resource in disguise. Compost turns scraps into soil. Reusing items saves resources. Aim for zero waste. It’s better for everyone.
Diverse Approaches To Green Permaculture
Green permaculture offers varied practices for sustainable living. It adapts to different environments and needs. This makes it versatile and accessible. Whether in cities, rural areas, or communities, permaculture provides tailored solutions. Each approach brings unique benefits and challenges.
Urban Permaculture
Urban permaculture transforms city spaces into green havens. Rooftop gardens and vertical farming thrive in limited spaces. This method reduces food miles and enhances local food security. Urban residents connect with nature through small-scale gardening. They can grow herbs, vegetables, and fruits in containers.
Community gardens foster cooperation among city dwellers. Such spaces become places for learning and sharing. Neighbors exchange skills and produce. This strengthens community bonds and promotes sustainability.
Rural Permaculture
Rural permaculture harnesses large land areas for sustainable agriculture. It integrates livestock, crops, and natural ecosystems. This approach minimizes waste and maximizes resources. Traditional farming techniques blend with modern permaculture methods. This ensures soil fertility and biodiversity.
Farmers use techniques like crop rotation and cover cropping. These practices maintain soil health and prevent erosion. Permaculture in rural areas supports local economies. It provides employment and food security for rural communities.
Community-based Permaculture
Community-based permaculture emphasizes collaboration and shared resources. It empowers neighborhoods to work together for sustainability. This approach fosters resilience and self-reliance. Communities design and manage local projects. They might start a shared garden or composting program.
Workshops and events spread permaculture knowledge. These gatherings encourage participation and foster a sense of belonging. Community-based permaculture creates a network of shared wisdom and support. It builds a foundation for sustainable living practices.
Benefits Of Green Permaculture
Green permaculture offers many benefits. It integrates sustainable practices into daily life. It supports the environment, economy, and society. Let's explore these benefits in detail.
Environmental Impact
Green permaculture promotes biodiversity. It uses natural resources wisely. This reduces waste and pollution. Permaculture farms improve soil health. Healthy soil absorbs more carbon. This helps combat climate change.
Water conservation is another advantage. Permaculture designs capture rainwater. They minimize runoff and erosion. This protects local waterways. Wildlife habitats thrive in permaculture systems. They provide shelter and food.
Economic Advantages
Permaculture reduces farming costs. It uses fewer chemicals and machinery. This lowers input expenses. Farmers save money over time. Sustainable practices improve crop yields. More produce means more income.
Local communities benefit too. Permaculture creates jobs in farming and education. It supports local markets and businesses. This strengthens the local economy.
Social And Cultural Benefits
Green permaculture fosters community spirit. People work together on shared projects. This builds strong bonds and networks.
Educational programs teach valuable skills. They inspire sustainable living. Cultural traditions are preserved through permaculture practices. They connect people to their heritage.
Permaculture promotes healthier lifestyles. Fresh, organic produce is accessible. This improves nutrition and well-being.
Challenges In Implementing Permaculture
Permaculture offers a sustainable way to design agricultural systems. Yet, its implementation often faces significant obstacles. Understanding these challenges can help enthusiasts and practitioners make informed decisions. Overcoming these hurdles requires patience and strategic planning.
Climate And Soil Conditions
Climate greatly influences permaculture practices. Regions with extreme weather pose unique challenges. Heavy rains can wash away soil. Droughts can dry out plants. Soil type also plays a critical role. Sandy soil drains water quickly. Clay soil retains too much moisture. Both require careful management for successful permaculture.
Knowledge And Skill Requirements
Permaculture is not just gardening. It involves complex planning and design. Many need training to understand its principles. Courses and workshops can help. They provide essential skills. Applying permaculture techniques demands practice and patience. Mistakes can lead to wasted resources. Continuous learning is crucial for success.
Community And Policy Barriers
Community support is vital for permaculture projects. Some communities resist change. They may prefer traditional farming methods. Building relationships takes time. Policies can also hinder progress. Zoning laws might restrict permaculture designs. Advocacy and education can help change perceptions. Working with local authorities can ease policy constraints.
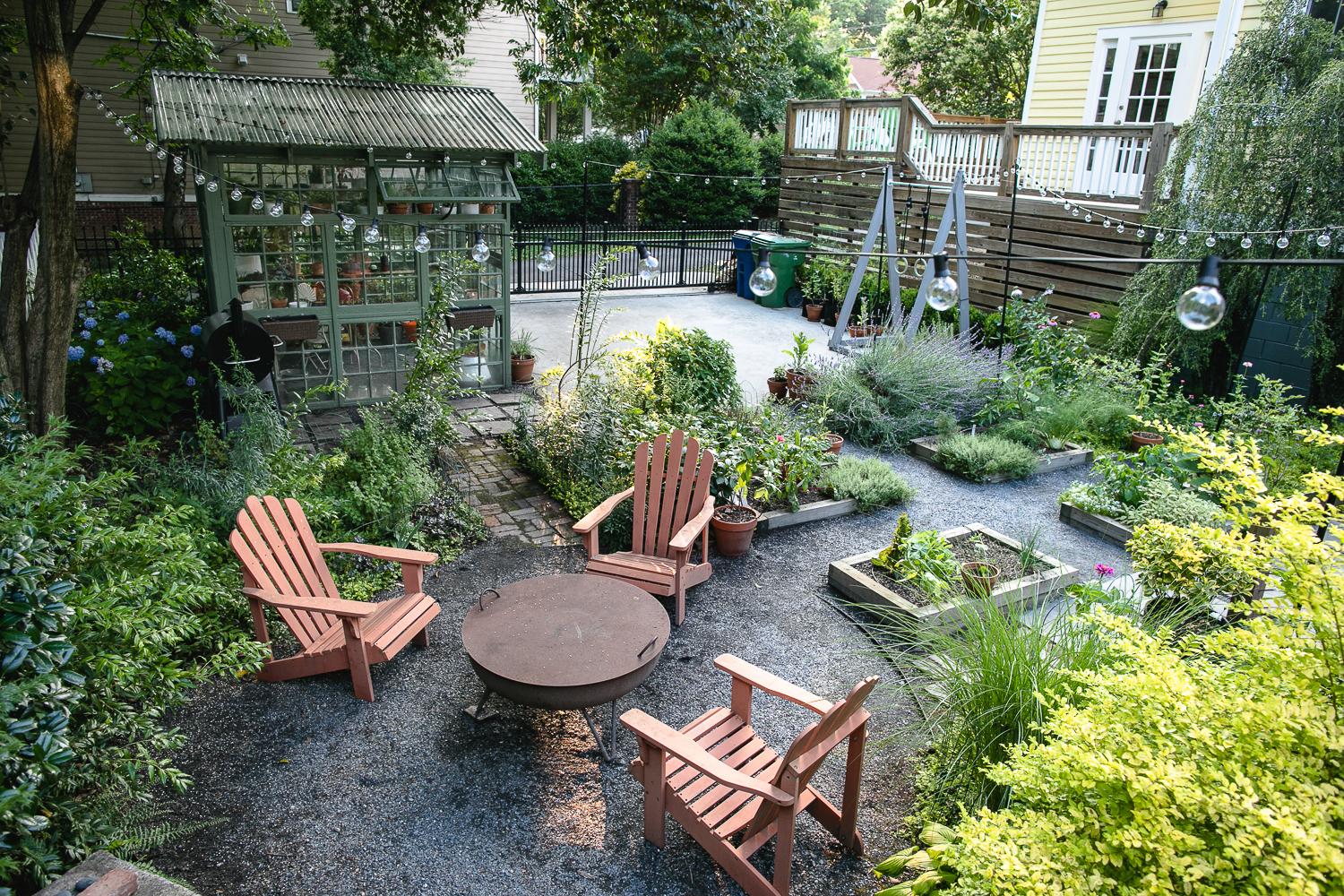

Credit: shadesofgreenpermaculture.com
Case Studies
Permaculture is transforming how we interact with our environment. Shades of Green Permaculture offers sustainable solutions for diverse settings. Their case studies show practical applications and inspiring results. Let's explore some successful projects.
Successful Urban Permaculture Projects
Urban areas face unique challenges in sustainability. Shades of Green Permaculture addresses these with innovative strategies. One project revitalized a neglected city park. They introduced native plants and rain gardens. This improved biodiversity and reduced stormwater runoff. A rooftop garden in a busy city center showcases another success. It provides fresh produce and a green oasis for residents. These urban projects demonstrate the possibilities for city environments.
Innovative Rural Permaculture Initiatives
Rural areas offer different opportunities for permaculture. Shades of Green Permaculture harnesses these with creative approaches. A small farm transformed barren land into a thriving ecosystem. They implemented crop rotation and natural pest control. This increased productivity and soil health. Another project focused on water management. A rural property installed a pond system for irrigation. This ensured water availability even in dry seasons. These rural initiatives highlight the power of permaculture to enhance landscapes.
Future Of Permaculture
Permaculture is evolving rapidly, shaping a sustainable future. It integrates ecological design principles, aiming to build harmonious systems. The future of permaculture holds exciting possibilities for our planet.
Technological Innovations
Innovations in technology are transforming permaculture practices. Drones help monitor plant growth and soil health efficiently. They provide accurate data, enhancing crop management and reducing labor. Smart sensors track soil moisture levels and nutrient content. This data helps optimize water usage and improve yield. Vertical farming technologies are gaining traction. They maximize space, supporting urban permaculture efforts. These advancements boost productivity while maintaining ecological balance.
Global Adoption And Trends
Permaculture principles are spreading worldwide. Different regions adapt these principles to local climates. In Africa, permaculture helps combat desertification and improve food security. Asian countries integrate traditional farming with modern permaculture techniques. Europe sees a rise in community-based permaculture projects. These initiatives foster collaboration and sustainable living. The global shift towards eco-friendly practices fuels permaculture adoption. Educational programs and workshops increase awareness among communities. This trend signifies a growing commitment to sustainable agriculture.
Credit: shadesofgreenpermaculture.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Permaculture In Green Living?
Permaculture in green living is a sustainable design philosophy. It focuses on mimicking natural ecosystems. This approach promotes biodiversity, soil health, and resource efficiency. It integrates land, resources, people, and the environment. Ultimately, permaculture aims to create harmonious and self-sustaining habitats.
How Does Permaculture Benefit The Environment?
Permaculture benefits the environment by enhancing biodiversity and soil health. It reduces waste and promotes resource conservation. This sustainable practice supports natural ecosystems. It minimizes harmful environmental impacts. Additionally, permaculture fosters resilience against climate change.
Can Permaculture Be Applied In Urban Areas?
Yes, permaculture can be applied in urban areas. It involves designing sustainable green spaces. Techniques include rooftop gardens and vertical farming. Urban permaculture enhances biodiversity and food production. It also promotes community engagement and environmental awareness.
What Are Common Permaculture Practices?
Common permaculture practices include companion planting and crop rotation. They also involve water conservation and composting. These practices enhance soil health and biodiversity. They promote sustainable resource use. Additionally, they focus on creating self-sustaining ecosystems.
Conclusion
Exploring shades of green permaculture enriches our connection to nature. It provides sustainable solutions for modern challenges. Choosing permaculture nurtures ecosystems and empowers communities. Adopting these practices leads to healthier lives and environments. Each green shade offers unique benefits and possibilities.
Dive deeper into permaculture to understand its potential. Simple steps can transform spaces and minds. Embrace permaculture and contribute positively to the planet. Start small, grow big. Remember, every action counts. Permaculture isn't just farming; it's a way of life.
Explore, learn, and implement. Your efforts can make a difference. Let's walk towards a greener future together.

Comments
Post a Comment