If you’ve ever wanted a garden that practically takes care of itself while bursting with life and productivity, understanding plant guilds is the key. Imagine your garden as a team where each plant plays a special role—some protect, some nourish, and others attract helpful insects—all working together to create a healthy, thriving ecosystem.
This isn’t just a dream; it’s the magic of plant guilds. By learning how to choose the right plants to support each other, you can turn your garden into a natural powerhouse that needs less work and gives you more abundance. Curious to dive deeper and discover exactly how to build these vibrant plant communities? Check out The Guild Method: How Permaculture Principles Create Abundant Gardens. This guide breaks down everything you need to know about creating your own self-sustaining garden using proven permaculture principles. Ready to transform your garden into a lush, balanced paradise? Let’s explore how plant guilds can change the way you grow.

Credit: www.permalogica.com
Introduction To Plant Guilds And Their Purpose
Plant guilds are a powerful way to grow healthy, abundant gardens. They come from permaculture principles and focus on teamwork among plants. Each guild has a central plant supported by other plants that help it thrive. This method creates natural balance and improves garden health.
Understanding how plant guilds work can help gardeners build self-sustaining ecosystems. These ecosystems use fewer chemicals and less effort while producing more food and beauty.
Understanding The Concept Of Plant Guilds
A plant guild is a group of plants growing together to support each other. At its center is the "Star Player", a main plant like a fruit tree or vegetable. Around it grow companion plants that serve specific roles.
Dynamic accumulators: Plants like comfrey that gather nutrients from deep soil layers.
Pollinator attractors: Flowers that bring bees and beneficial insects.
Natural pest deterrents: Plants such as garlic or chives that repel harmful bugs.
Ground covers: Plants that protect soil and reduce weeds, like clover.
Each plant’s role creates a balanced, supportive community. This reduces the need for fertilizers and pesticides. The guild grows stronger and more resilient over time.
How Plant Guilds Enhance Garden Health Naturally
Plant guilds improve garden health by mimicking natural ecosystems. They:
Boost soil fertility: Through nutrient cycling and natural mulch.
Encourage beneficial insects: Attract predators that control pests.
Reduce diseases: Diverse plants limit the spread of pathogens.
Conserve water: Ground covers and layered plants reduce evaporation.
This approach supports organic and sustainable gardening. It encourages biodiversity and creates a thriving habitat for plants and wildlife.
Benefit | How It Works |
|---|---|
Soil Health | Dynamic accumulators recycle nutrients to the surface |
Pest Control | Companion plants repel or attract beneficial insects |
Water Conservation | Layered plants and ground covers retain moisture |
Biodiversity | Multiple species create a balanced ecosystem |
By using plant guilds, gardeners create abundant and resilient gardens. This method aligns with the teachings of The Guild Method: How Permaculture Principles Create Abundant Gardens by Ace Bailey, which explains how to select and combine plants effectively.
Key Features Of Plant Guilds That Boost Garden Health
Plant guilds create a balanced and thriving garden ecosystem. They combine various plants with unique roles that work together. This cooperation enhances soil, controls pests naturally, and conserves water. Understanding these key features helps gardeners design more productive and resilient gardens.
Diverse Plant Roles: Support, Protection, And Nutrition
Each plant in a guild serves a special purpose. The central “Star Player” plant anchors the group.
Support plants provide shade, structure, or physical protection.
Protective plants repel pests and diseases.
Nutritional plants fix nitrogen or improve soil nutrients.
This diversity creates a natural balance. Plants help each other grow stronger and healthier.
Natural Pest Control Through Companion Plants
Companion plants act as natural pest repellents. They confuse or deter harmful insects.
Examples include:
Garlic and chives repel aphids and beetles.
Daffodils discourage rodents and deer.
Herbs like thyme and basil attract beneficial insects that eat pests.
This reduces the need for chemical pesticides and protects plant health.
Soil Enrichment And Improved Nutrient Cycling
Guild plants improve soil quality naturally. Some plants gather nutrients from deep soil layers.
Plant Type | Role in Soil | Example |
|---|---|---|
Dynamic Accumulators | Bring minerals to surface | Comfrey |
Nitrogen Fixers | Add nitrogen to soil | Clover |
Mulch Producers | Provide organic matter | Leaves from trees or shrubs |
These processes boost nutrient cycling and support healthy plant growth.
Water Conservation Via Strategic Plant Grouping
Plant guilds conserve water by grouping plants with similar needs.
Deep-rooted plants draw water from underground.
Shallow-rooted plants reduce surface evaporation.
Mulching plants keep soil moist and cool.
This arrangement helps gardens use water efficiently and stay resilient during dry spells.
Pricing And Affordability: Starting Your Own Plant Guild
Starting a plant guild offers a cost-effective path to a thriving garden. Plant guilds focus on natural partnerships between plants, reducing the need for expensive inputs. The initial investment often balances out with long-term benefits. Understanding the costs helps gardeners plan better and achieve success without overspending.
Cost Comparison: Plant Guilds Vs Traditional Gardening Practices
Traditional gardening often requires buying fertilizers, pesticides, and separate plants. Plant guilds reduce these costs by using companion plants that support each other naturally. The table below shows a basic comparison:
Expense | Traditional Gardening | Plant Guilds |
|---|---|---|
Seeds and Plants | High (multiple species, non-synergistic) | Moderate (carefully chosen companions) |
Fertilizers | Regular purchase needed | Reduced (natural soil enrichment) |
Pesticides | Frequent use required | Minimal (natural pest control plants) |
Water Usage | High | Lower (plants support moisture retention) |
Plant guilds save money by reducing external inputs and promoting plant health.
Affordable Plant Selections For Effective Guilds
Choosing budget-friendly plants helps build a strong guild without high costs. Many companion plants are easy to find and grow.
Clover: Fixes nitrogen and improves soil quality.
Comfrey: Acts as a dynamic accumulator, pulling nutrients from deep soil.
Garlic and Chives: Natural pest deterrents.
Daffodils: Help keep unwanted animals away.
Starting with these plants lowers expenses and enhances garden health. The “Star Player” plant anchors the guild and can be a fruit tree or vegetable suited to your climate.
Long-term Savings Through Reduced Inputs
Plant guilds reduce the need for fertilizers, pesticides, and extra watering. This lowers ongoing expenses.
Companion plants enrich soil naturally.
Natural pest control lowers or eliminates chemical use.
Improved soil moisture reduces irrigation costs.
Increased biodiversity improves garden resilience and yield.
Over time, these benefits save money and effort. Investing in a plant guild creates a sustainable garden system that pays off year after year.
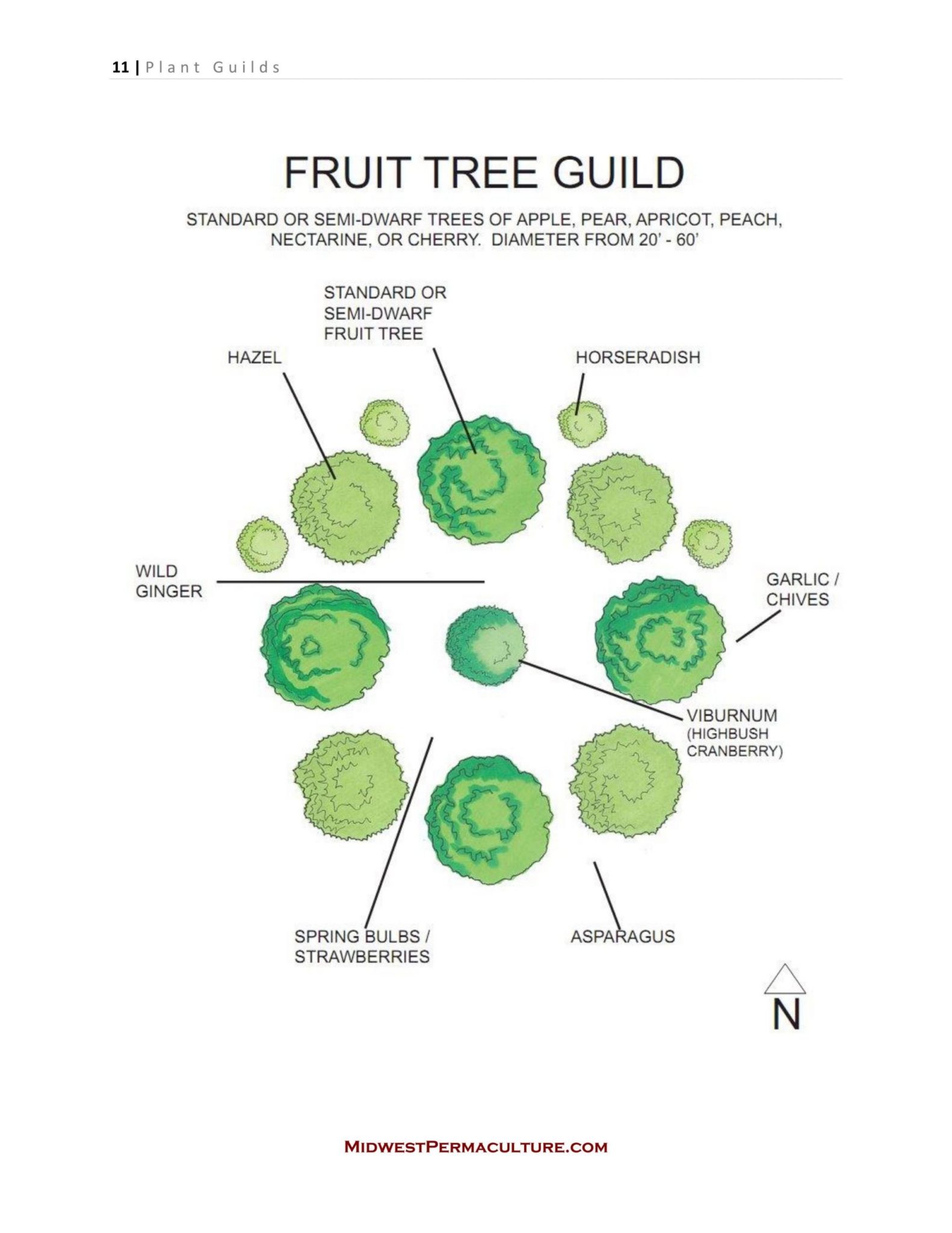
Credit: midwestpermaculture.com
Pros And Cons Of Using Plant Guilds Based On Real-world Usage
Plant guilds create a network of plants that support one another. This method builds garden ecosystems that are resilient and productive. Real-world use shows clear benefits and some challenges. Understanding both helps gardeners apply guilds effectively.
Advantages: Enhanced Garden Resilience And Biodiversity
Plant guilds boost garden health by increasing diversity and balance.
Improved soil fertility: Companion plants add nutrients and prevent erosion.
Natural pest control: Certain plants repel pests or attract beneficial insects.
Better water retention: Layered planting reduces evaporation and conserves moisture.
Increased productivity: Plants support each other’s growth, yielding more food.
Stronger resilience: Diverse species withstand weather extremes and diseases better.
These factors create a garden that thrives with less human input. Biodiversity attracts wildlife and maintains ecological balance.
Challenges: Planning Complexity And Maintenance Considerations
Designing a plant guild requires careful planning and knowledge.
Choosing the “Star Player”: Selecting the central plant needs understanding of local climate and soil.
Matching companion plants: Plants must complement each other’s needs and growth habits.
Space management: Guilds need room for layers without overcrowding.
Initial setup time: Establishing guilds demands more effort than simple planting.
Ongoing maintenance: Regular pruning and monitoring keep the guild balanced and healthy.
These challenges can slow down beginners. Gardeners must learn permaculture principles for success.
Common Mistakes And How To Avoid Them
Errors in guild design often reduce benefits and cause frustration.
Ignoring plant compatibility: Avoid mixing plants with conflicting water or nutrient needs.
Overcrowding: Space plants adequately to prevent competition and disease.
Neglecting soil health: Test soil and improve it before planting guilds.
Forgetting maintenance: Schedule regular care to manage growth and pest control.
Skipping observation: Watch how plants interact and adjust the guild as needed.
Following these tips helps create successful, thriving guilds.
Specific Recommendations For Ideal Users And Gardening Scenarios
Plant guilds offer versatile solutions for various gardening needs. Their design suits different users and environments. Understanding where and how to apply guilds improves garden success and sustainability. This section highlights tailored advice for common gardening situations and users.
Best Practices For Home Gardeners And Urban Growers
Home gardeners and urban growers benefit greatly from plant guilds. These systems maximize space and boost biodiversity. The key is choosing the right Star Player—a central plant that anchors the guild.
Select compact or dwarf varieties for limited spaces.
Use companion plants like clover, garlic, and chives for pest control and soil health.
Layer plants vertically to optimize sunlight and space.
Focus on low-maintenance, drought-tolerant species.
Raised beds or containers work well for urban settings. They provide control over soil quality and drainage.
Implementing Plant Guilds In Small-scale Farms
Small-scale farms gain from guilds by improving productivity and resilience. Guilds reduce the need for synthetic inputs by enhancing natural processes.
Identify a dominant crop as the Star Player, such as fruit trees or vegetables.
Integrate dynamic accumulators like comfrey to recycle nutrients.
Include pest-repellent plants such as daffodils or garlic.
Design guilds to support crop rotation and soil regeneration.
Planning guilds with diverse plant roles helps maintain soil fertility and controls pests naturally.
Adapting Plant Guilds To Different Climate Zones
Climate affects plant guild success. Adjust plant choices and guild structure to fit local conditions.
Climate Zone | Recommended Star Players | Companion Plants | Key Adaptations |
|---|---|---|---|
Temperate | Apple, Peach | Clover, Comfrey, Garlic | Seasonal pruning, mulch for frost protection |
Arid | Pomegranate, Olive | Lavender, Daffodils, Chives | Drought-tolerant species, deep mulching |
Tropical | Mango, Papaya | Legumes, Marigold, Basil | Shade layering, pest-resistant plants |
Choosing plants adapted to your climate ensures guild health and abundance. Mulching and layering help balance moisture and temperature extremes.

Credit: www.alohafoodforest.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Plant Guilds In Gardening?
Plant guilds are groups of plants that support each other’s growth. They create a balanced ecosystem. Each plant has a specific role, like fixing nitrogen or repelling pests, making the garden healthier and more productive.
How Do Plant Guilds Improve Soil Health?
Plant guilds enhance soil by adding nutrients and organic matter. Nitrogen-fixing plants enrich the soil naturally. Deep-rooted plants break up compacted soil, improving aeration and water absorption, leading to stronger plant growth.
Which Plants Are Best For Creating Guilds?
Ideal guild plants include nitrogen-fixers, dynamic accumulators, ground covers, and pest repellents. Examples are clover, comfrey, mulch plants, and marigolds. Combining these plants supports growth and protects the garden naturally.
Can Plant Guilds Reduce Pest Problems?
Yes, plant guilds reduce pests by attracting beneficial insects and repelling harmful ones. Companion plants like garlic and marigolds act as natural pest deterrents, minimizing the need for chemical pesticides in your garden.
Conclusion
Plant guilds build strong, healthy gardens naturally. They help plants grow better together. Using guilds means fewer pests and richer soil. This method saves time and effort for gardeners. To deepen your knowledge, consider reading The Guild Method: How Permaculture Principles Create Abundant Gardens. It guides you step-by-step on creating thriving garden ecosystems. Start small and watch your garden flourish with guild planting. Nature works best when plants support each other. Try guilds and enjoy a more vibrant garden today.

Comments
Post a Comment