Permaculture principles guide sustainable living and farming. They focus on working with nature, not against it.
Permaculture is more than just a gardening method. It’s a philosophy for living in harmony with our environment. These principles help us create systems that sustain both people and the planet. They show us how to use resources wisely and reduce waste.
By following permaculture principles, we can grow food, build homes, and live our lives in a way that benefits the Earth. This approach is vital for a future where humans and nature thrive together. Join us as we explore these principles and discover how they can transform our world.
Credit: permacultureprinciples.com
Introduction To Permaculture
Permaculture is a system for designing sustainable living environments. It integrates harmoniously with nature. The word combines "permanent" and "agriculture". It emphasizes working with nature, not against it. This principle is crucial for creating self-sustaining ecosystems. Let's delve into the origins and core ethics of permaculture.
Origins Of Permaculture
Permaculture originated in the 1970s. It was developed by Bill Mollison and David Holmgren in Australia. They aimed to create a way of living that was both productive and sustainable. Their approach was rooted in observing natural ecosystems. They believed nature already had the answers. Their work laid the foundation for permaculture as we know it today.
They published their ideas in a book titled Permaculture One. This book became a cornerstone for the permaculture movement. It inspired many to adopt these principles globally. Today, permaculture has spread to every continent. It influences not just agriculture but also urban planning and community development.
Core Ethics
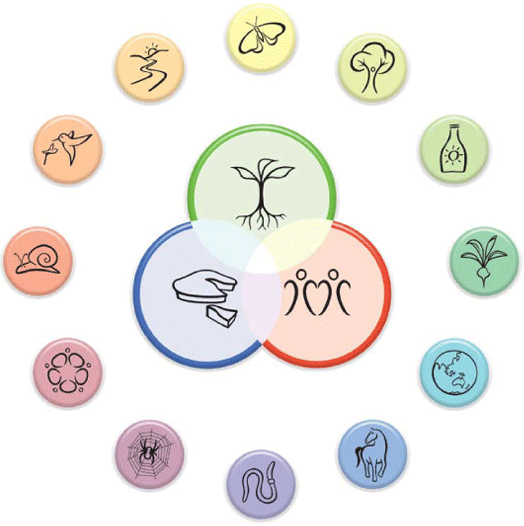
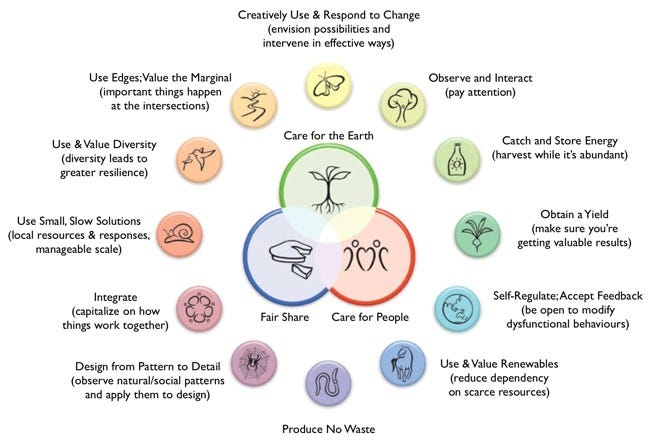
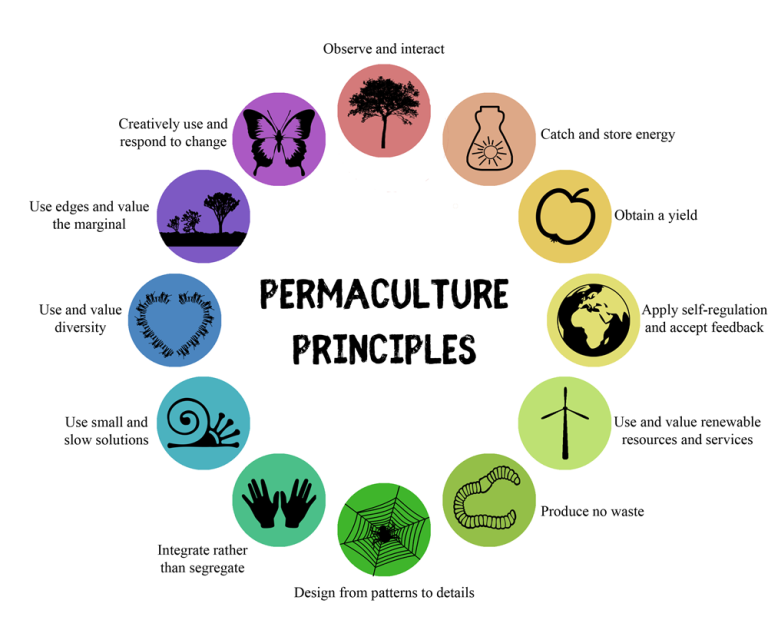
Permaculture is built upon three core ethics. These ethics guide every decision within a permaculture design.
Earth Care: This ethic emphasizes the importance of nurturing the earth. It involves practices that maintain and improve soil health, conserve water, and protect biodiversity.
People Care: This principle focuses on the well-being of people. It encourages community building, sharing resources, and ensuring that everyone's basic needs are met.
Fair Share: Also known as "return of surplus," this ethic promotes the distribution of surplus resources. It ensures that excess is returned to the earth or shared within the community.
These core ethics are the foundation of permaculture. They help create a balanced and sustainable way of living. By adopting these ethics, individuals can contribute to a healthier planet and community.
Credit: medium.com
Designing Your Permaculture Garden
Permaculture principles focus on creating sustainable and self-sufficient gardens. These principles emphasize using natural resources efficiently. Design your garden to work with nature, not against it.
Creating a permaculture garden involves thoughtful planning. It's not just about planting seeds. You need to observe, understand, and work with nature. This makes your garden sustainable and productive.
Site Assessment
Start with a site assessment. Observe your garden space. Note the sunlight, wind patterns, and soil type. Identify areas with good drainage. Check for slopes and flat areas. Understand the microclimates in your garden. This helps in placing plants in the right spots.
Zoning Techniques
Use zoning techniques for better garden design. Divide your garden into zones. Zone 1 is closest to your home. This is for plants needing daily attention. Zone 2 is for less demanding plants. Zone 3 is for orchards and larger crops. Zone 4 is semi-wild, for forage and timber. Zone 5 is wild, left for nature. This zoning helps in efficient garden management. ```
Soil Health And Fertility
Soil health and fertility are the foundations of a thriving permaculture system. Good soil supports plant growth, retains water, and nurtures beneficial organisms. Focusing on soil health ensures long-term productivity and ecological balance. By enriching the soil, we can create a robust and sustainable environment.
Composting Methods
Composting turns organic waste into valuable nutrient-rich soil. There are several composting methods to choose from, each with its unique benefits. Hot composting is fast and effective. It requires turning the pile regularly to maintain heat. Cold composting takes longer but needs less maintenance. It’s perfect for those with less time. Vermicomposting uses worms to break down organic material. It produces rich, fertile worm castings.
Bokashi composting is another option. It uses fermentation to decompose waste. This method works indoors and handles meat and dairy scraps. Each method has its strengths, so choose the one that fits your needs best.
Soil Building Strategies
Building healthy soil is a continuous process. One effective strategy is mulching. Mulch protects the soil, retains moisture, and adds organic matter. Use leaves, straw, or wood chips as mulch. Cover cropping is another valuable technique. Plant cover crops like clover or rye to enrich the soil. They fix nitrogen and improve soil structure.
Crop rotation prevents soil depletion. Rotate plants to avoid nutrient exhaustion. Avoid planting the same crops in the same spot each year. Adding compost regularly boosts soil fertility. It introduces beneficial microorganisms and nutrients. Practicing no-till gardening helps maintain soil structure. It reduces erosion and preserves soil life.
Water Management
Effective water management is crucial in permaculture. It ensures sustainable use of water resources. Efficient water management techniques support healthy plant growth. They help maintain soil health. Two key aspects of water management are rainwater harvesting and irrigation techniques.
Rainwater Harvesting
Rainwater harvesting involves collecting and storing rainwater. This water can be used for irrigation and other needs. It reduces dependency on municipal water. It also minimizes water wastage. Here are some methods:
Rain Barrels: These are simple containers placed under downspouts. They collect rainwater from roofs.
Rain Gardens: These are shallow, planted depressions. They absorb rainwater runoff from roofs, driveways, and lawns.
Swales: These are shallow ditches on contour lines. They slow down water runoff and allow it to soak into the ground.
Using these methods helps maintain the water cycle. It supports the local ecosystem. It also ensures plants receive natural water.
Irrigation Techniques
Proper irrigation techniques are vital in permaculture. They ensure efficient water use. They also promote healthy plant growth. Here are some common irrigation methods:
Drip Irrigation: This method delivers water directly to plant roots. It reduces water wastage and evaporation.
Soaker Hoses: These hoses release water slowly along their length. They are effective for garden beds and rows of plants.
Mulching: This involves covering the soil with organic materials. It reduces water evaporation and keeps the soil moist.
These techniques conserve water. They ensure plants receive adequate hydration. They also help maintain soil structure and health.
Incorporating effective water management practices in permaculture is essential. It promotes sustainability. It supports a thriving ecosystem.
Plant Selection And Diversity
Plant selection and diversity are vital in permaculture. They help create a balanced ecosystem. By choosing the right plants, you can improve soil health. You can also attract beneficial insects. A diverse garden is more resilient to pests and diseases.
Native Plants
Native plants are adapted to your local climate. They need less water and care. These plants have natural resistance to local pests. They support local wildlife, including birds and insects. Native plants also help maintain the natural ecosystem. They prevent invasive species from taking over.
Companion Planting
Companion planting means growing plants that benefit each other. Some plants repel pests. Others attract beneficial insects. For example, planting basil with tomatoes improves their growth. Marigolds can keep harmful insects away from vegetables. Companion planting boosts plant health and yield.
Credit: kukuapermaculture.org
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is a core principle of permaculture. It aims to reduce energy consumption and utilize resources effectively. By integrating energy-efficient practices, we can create sustainable and self-sufficient systems. This not only benefits the environment but also lowers energy costs.
Renewable Energy Sources
Using renewable energy sources is key in permaculture. Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. Wind turbines harness wind power to generate energy. Hydropower systems use flowing water to produce electricity. These sources are sustainable and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. They minimize carbon footprint and support a green lifestyle.
Passive Solar Design
Passive solar design optimizes the use of sunlight in building construction. It involves strategic placement of windows and walls. South-facing windows maximize natural light and heat. Proper insulation keeps the interior warm in winter and cool in summer. Thermal mass materials store and release solar energy. This reduces the need for artificial heating and cooling. It leads to significant energy savings.
Sustainable Living Practices
Permaculture principles focus on creating sustainable living practices that benefit both humans and the environment. These practices help in building a self-sufficient and eco-friendly lifestyle. By adopting such methods, you can reduce your carbon footprint and promote a healthier planet. Let's explore some key sustainable living practices in permaculture.
Waste Reduction
Reducing waste is crucial in permaculture. Start by minimizing disposable items. Choose reusable products like cloth bags, metal straws, and glass containers. Composting organic waste is another effective way. It turns food scraps into valuable soil nutrients. This reduces landfill waste and enriches your garden soil. Also, buy products with minimal packaging. Choose items that come in recyclable or biodegradable containers. This small step helps decrease overall waste.
Resource Recycling
Resource recycling is vital in sustainable living. Reuse materials whenever possible. Old furniture can be refurbished instead of discarded. Glass jars make excellent storage containers. Collect rainwater for gardening. This practice conserves water and reduces your utility bills. Turn kitchen scraps into compost. It cuts down waste and nourishes plants. Recycling extends the life of resources and reduces the need for new materials.
Community And Social Aspects
Permaculture is not just about sustainable gardening. It also focuses on building strong communities. These principles promote social interaction, cooperation, and shared responsibility. By fostering community connections, permaculture can create resilient and supportive networks.
Community Gardens
Community gardens bring people together. They create shared spaces for growing food. Neighbors can connect and collaborate. These gardens provide fresh produce, promoting health and well-being. They also reduce food costs for families. Volunteers often manage these spaces, building a sense of ownership and pride. Community gardens can transform empty lots into vibrant, green areas. They also serve as educational sites for sustainable practices.
Educational Outreach
Educational outreach is vital in permaculture. Teaching others about sustainable living can spread knowledge. Workshops and classes can engage the community. Schools can include permaculture in their curriculum. This helps children learn about the environment early. Community centers can host events and talks. These sessions can cover topics like composting, water conservation, and organic farming. Sharing information helps build a knowledgeable and proactive community.
Challenges And Solutions
Permaculture principles offer sustainable solutions for farming and gardening. Yet, they come with their challenges. Understanding these challenges and finding solutions is key to success. Below, we explore two main areas: Pest Management and Climate Adaptation.
Pest Management
Managing pests in a permaculture system can be difficult. Traditional methods often rely on chemicals. Permaculture promotes natural solutions, which need more effort and knowledge.
Solution: Introduce natural predators to control pests. For example:
Ladybugs to eat aphids
Frogs and toads to eat insects
Bats to control mosquito populations
Companion planting also helps. Planting certain crops together can repel pests. For instance, marigolds planted with tomatoes deter nematodes.
Another method is crop rotation. This reduces pest buildup in the soil. Rotate different crops each season. This disrupts pest life cycles.
Climate Adaptation
Climate change affects weather patterns. This poses a risk to permaculture systems. Droughts, floods, and extreme temperatures can damage crops.
Solution: Use water management techniques. These include:
Building swales to capture rainwater
Installing rain barrels to store water
Implementing drip irrigation systems to reduce water use
Choose climate-resilient plants. Some plants are better suited to extreme conditions. For example:
Condition | Resilient Plants |
|---|---|
Drought | Succulents, Lavender, Sage |
Flood | Rice, Watercress, Taro |
Cold | Kale, Carrots, Brussels Sprouts |
Creating microclimates can also help. Use structures like greenhouses or shade cloths. These protect plants from harsh conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Permaculture Principles?
Permaculture principles are guidelines for designing sustainable ecosystems. They focus on energy efficiency, natural resources, and self-sufficiency. These principles aim to create harmonious relationships between humans and nature.
How Does Permaculture Benefit The Environment?
Permaculture benefits the environment by promoting biodiversity and reducing waste. It encourages the use of renewable resources and enhances soil fertility. This sustainable approach helps combat climate change.
Can Permaculture Be Applied In Urban Areas?
Yes, permaculture can be applied in urban areas. It includes practices like rooftop gardens, vertical farming, and community gardens. Urban permaculture helps in maximizing space and promoting local food production.
What Are Some Examples Of Permaculture Techniques?
Examples of permaculture techniques include companion planting, rainwater harvesting, and composting. These techniques aim to create a sustainable and self-sufficient ecosystem. They help in conserving resources and improving soil health.
Conclusion
Permaculture principles help create sustainable and self-sufficient systems. They focus on working with nature. Small changes can make a big difference. Start applying these principles in your daily life. Observe, adapt, and enjoy the benefits. Your garden or farm will thrive.
Healthy ecosystems support healthy communities. Embrace permaculture for a greener future. It’s simple, effective, and rewarding.

Comments
Post a Comment